Leave Your Message
Air Energy Heat Pumps are innovative solutions for efficient heating and cooling. According to John Smith, an expert in HVAC technology, "Air Energy Heat Pumps can significantly reduce energy consumption." This technology utilizes outdoor air to heat or cool a space. It works by transferring heat from the air, even in cold weather, making it versatile.
These systems are becoming increasingly popular in residential and commercial settings. They provide a sustainable alternative to traditional heating methods. Many people might think that performance declines in winter. However, Air Energy Heat Pumps are designed to operate effectively in various conditions.
The installation process can be complex. Homeowners must consider their specific needs. Not every system will fit every home. Some challenges may arise, such as sizing and efficiency concerns. As with any technology, careful evaluation is essential for optimal performance.

An air energy heat pump is a device that transfers heat from the outside air to your home. It uses refrigerants to absorb and release heat. This process allows you to heat or cool your living space efficiently. During colder months, it extracts heat even when outside temperatures drop.
The system works like a refrigerator but in reverse. It pulls in air, uses a compressor, and then channels warm air indoors. In summer, it functions as an air conditioner. The heat pump expels hot air outside, cooling your space. This dual functionality makes it a versatile option for many households.
However, air energy heat pumps don’t always operate perfectly. Efficiency can drop in extreme cold. They require backup heating systems during harsh winters. Maintenance is also crucial for optimal performance. Regular checks can help catch issues early, allowing for smooth operation year-round.
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Air Source Heat Pump |
| Function | Heating and Cooling of Spaces |
| Energy Source | Extracts heat from outdoor air |
| Efficiency Rating | Up to 300-400% (COP) |
| Installation Location | Outside of the building |
| Typical Uses | Residential heating, water heating, and cooling |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels |
| Lifespan | 15-20 years |
Air energy heat pumps are gaining popularity due to their efficiency and sustainability. Understanding their key components is crucial for grasping how they function. Key parts include the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. Each plays a vital role in the heat pump’s operations.
The evaporator absorbs heat from the air, even in cold conditions. This heat is transferred to the refrigerant, which turns into gas. The compressor then raises the temperature and pressure of this gas, allowing it to flow into the condenser. Here, heat is released into the home, providing warmth. The expansion valve then regulates the refrigerant flow, preparing it to return to the evaporator.
Reports indicate that heat pumps are typically 3-4 times more efficient than traditional heating systems. However, performance can drop in extremely cold climates. Some studies highlight that efficiency may reduce significantly when temperatures fall below freezing. This can lead to higher energy consumption than expected. It's essential for users to consider local climate conditions when evaluating heat pump efficiency. Engaging with these aspects contributes to better energy decisions.
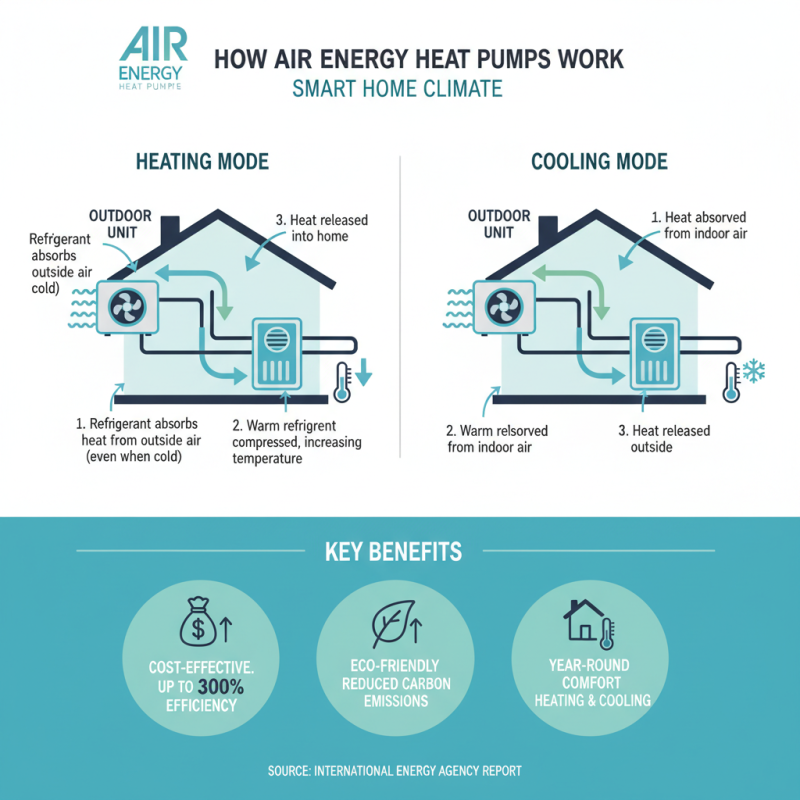
Air energy heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular for heating and cooling homes. They work by transferring heat from the air outside to inside your home. This process starts with a refrigerant absorbing heat from the air, even in cold conditions. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, these systems can achieve efficiencies of over 300%, making them a cost-effective choice for many households.
The operation of air energy heat pumps involves several steps. First, the outdoor air is drawn into the unit, where it passes over the evaporator coil. The refrigerant absorbs heat and turns into gas. Then, this gas is compressed, raising its temperature. Next, it moves to the condenser coil, where it releases heat into the indoor space. Finally, the refrigerant returns to a liquid state, completing the cycle. However, one must consider local climate conditions. In extremely cold areas, performance can drop, leading to lower efficiency.
In practice, installation challenges may arise. Finding the right size for your home is crucial. If the unit is too large or small, efficiency suffers. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning filters, is also essential. Failing to do so can lead to higher energy bills and reduced system lifespan, which many homeowners often overlook.
Air energy heat pumps are innovative systems that efficiently provide both heating and cooling. They work by transferring heat from the outside air into your home during the winter and reversing the process in summer. This dual functionality makes them a popular choice for year-round comfort.
One of the key advantages is energy efficiency. Air energy heat pumps can significantly reduce energy bills compared to traditional heating methods. They use electricity to move heat rather than generate it, leading to lower consumption. However, their efficiency can depend on outdoor temperatures. In extremely cold climates, performance may decrease, requiring additional heating sources.
Another benefit is their environmentally friendly nature. These systems produce fewer greenhouse gases than conventional gas or oil heating systems. Homeowners may also qualify for rebates and incentives by choosing these systems. Despite these advantages, there can be concerns regarding initial installation costs. Planning and choices in system design are vital to maximize their potential benefits. Balancing these features can lead to greater satisfaction over time.
Air energy heat pumps are becoming increasingly popular for heating and cooling. Their applications range from residential homes to commercial buildings. These systems extract heat from the air, even in cold temperatures. They can effectively provide warmth in winter and coolness in summer. Yet, they are not a one-size-fits-all solution.
One limitation is efficiency. In extremely cold climates, their performance can drop. This leads to increased energy consumption and higher costs. Homeowners might need a backup heating system. Additionally, installation requires careful consideration of space and airflow. Poor placement can reduce efficiency and increase wear and tear. These drawbacks highlight the necessity of proper planning.
Maintenance can also be tricky. Filters need regular cleaning or replacement. Ignoring maintenance can lead to efficiency loss over time. Users may find energy bills climbing due to neglect. It’s crucial to monitor performance regularly. A proactive approach ensures that the system operates effectively. Understanding these limitations helps users make informed decisions.