Leave Your Message
In recent years, the interest in sustainable heating solutions has grown significantly. Among these, the Water Heatpump stands out as a highly efficient option. Renowned expert in the field, Dr. Jane Smith, emphasizes its advantages, stating, “Water Heatpumps can transform energy efficiency in modern heating systems.” This technology utilizes water as a heat source or sink, providing an innovative solution to our energy needs.
Water Heatpumps operate by transferring heat from water to a building. They can extract heat from lakes, rivers, or even groundwater. This process not only offers lower operating costs but also reduces reliance on fossil fuels. However, there are challenges. The effectiveness of a Water Heatpump can vary depending on local climate conditions and water temperature. Users may need to invest in initial setup costs, which can be a barrier for some.
As the world moves towards greener technologies, the Water Heatpump presents an exciting opportunity. It opens up discussions on energy use and conservation. Yet, it is crucial to consider the environmental impact of water resources being utilized. As we explore options, a balanced approach is necessary for sustainable practices in the heating industry.

A water heat pump is a system that transfers heat from one place to another using water as the primary medium. It operates by extracting heat from the environment, such as groundwater or surface water, and then using that heat to provide heating or hot water for residential and commercial use. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can be more than 300% efficient, meaning they can produce three times the energy they consume.
These systems work through a cycle of evaporation and condensation. Water from a source is pumped into an evaporator, where it absorbs heat and turns into vapor. This vapor then moves to a compressor, which increases its pressure and temperature. Finally, the heated vapor passes through a condenser, releasing heat into the desired space or water system. While effective, the efficiency of a water heat pump can be influenced by seasonal water temperature variations, which may lead to performance issues in colder climates.
Research indicates that water heat pumps can reduce energy costs by 30-60% compared to traditional heating systems. However, installation can be complex and costly. Not all properties are suitable for this technology. It's essential to assess site-specific conditions. Sometimes, the initial enthusiasm can overshadow the practical challenges. Each installation may require considerable thought to avoid potential inefficiencies.
A water heat pump is an efficient system for heating and cooling spaces. It uses water as a medium to conduct heat. This process is largely dependent on its key components.
The evaporator is one of the most crucial parts. It absorbs heat from the surrounding water. When water passes through the evaporator, it changes to vapor. This vapor is then compressed to increase its temperature. The compressor plays a vital role here. It ensures that the heat is circulated effectively throughout the system.
Another essential component is the condenser. Here, the heated vapor releases its energy, warming up the water for use. A thermal expansion valve controls the flow of refrigerant. This ensures efficiency and proper functioning. Often, these components may not work ideally. Regular maintenance is necessary to avoid inefficiencies. Small issues can lead to performance drops. It's important to observe and assess these systems regularly.
| Component | Function | Material | Typical Efficiency Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat from water | Copper | 3.5 - 4.5 COP |
| Compressor | Increases temperature of refrigerant | Aluminum | 3.0 - 4.0 COP |
| Condenser | Releases heat to heating system | Copper | 4.0 - 5.0 COP |
| Expansion Valve | Controls refrigerant flow | Brass | N/A |
| Refrigerant | Transfers heat | Synthetic fluid | N/A |
Water heat pumps are fascinating devices that use water as a heat source or sink for heating and cooling. The operation begins with extracting heat from a water source, such as a lake, river, or ground. This process utilizes a heat exchanger to absorb heat from the water, even in colder temperatures. The extracted heat is then transferred to a refrigerant, which circulates through the system.
After the refrigerant absorbs the heat, it goes through compression, increasing its temperature. Once heated, the refrigerant travels to another heat exchanger inside the building. Here, it releases the heat into the environment, warming the air or water systems. It's quite interesting how a device can harness natural resources to regulate climate. However, the efficiency of this process can vary with the water temperature and system design.
While water heat pumps are efficient, they are not without challenges. Installation can be complex. Site selection is crucial for optimal performance. Sometimes, the water source might not reach the ideal temperature. These variables can affect overall effectiveness. It's essential to evaluate the local climate and resource availability. Understanding all these factors can lead to better decision-making and improved results in heating and cooling applications.
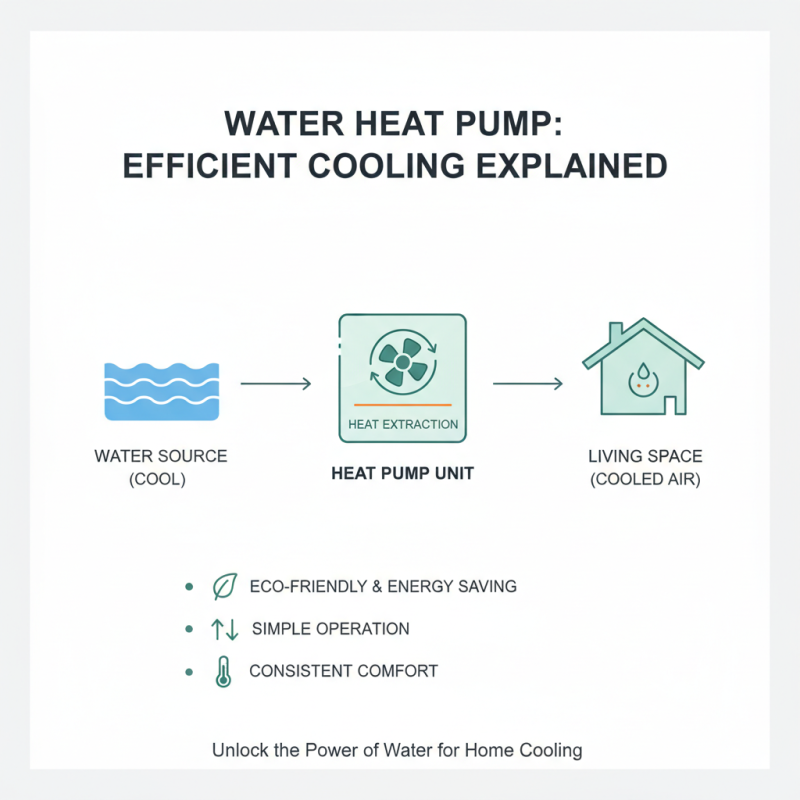
Water heat pumps are gaining popularity for their efficient cooling mechanisms. These systems extract heat from water sources and transfer it to a living space. The operational simplicity attracts many users. However, understanding how they cool effectively can demystify their value.
The cooling mechanism of water heat pumps relies on refrigeration cycles. The process starts with a refrigerant absorbing heat from the water. This chilled refrigerant then circulates through the evaporator. Data from the International Energy Agency indicates that heat pumps can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional cooling systems. This is particularly beneficial in regions with hot climates.
Tips: For maximum efficiency, consider regular maintenance. Clean filters and inspect water sources frequently. Small issues can escalate, leading to larger expenses. Being proactive saves money. Furthermore, ensure your system is appropriately sized for your space. Oversized units can lead to inefficiency and increased operating costs.
Water heat pumps are becoming popular in various applications due to their energy efficiency. They work by transferring heat from water sources, such as lakes or groundwater, to heat buildings. Their ability to harness renewable energy makes them an attractive option for both residential and commercial use.
One significant advantage of water heat pumps is their versatility. They can be used for heating, cooling, and even hot water production. This multifunctionality can lead to reduced energy costs. In colder climates, they can remain efficient by drawing heat from deeper water layers. However, installation can be complex and may require access to suitable water sources.
Additionally, water heat pumps can enhance indoor comfort. They provide consistent temperatures and reduce humidity levels. Yet, they might not be suitable for every location. Factors such as local climate and water availability can limit their effectiveness. Proper planning is essential for successful implementation. Users should consider potential challenges, including maintenance needs and initial costs.